The cost of electricity has been a crucial aspect of our lives for decades. As residents and businesses in Oklahoma, understanding the historical trends and evolution of electricity expenses can provide valuable insights into how energy consumption has changed over time. By examining past and present data, we can gain a deeper understanding of the factors influencing energy expenses and how we can navigate the future of energy consumption.
Historical Electricity Costs: Looking Back in Time
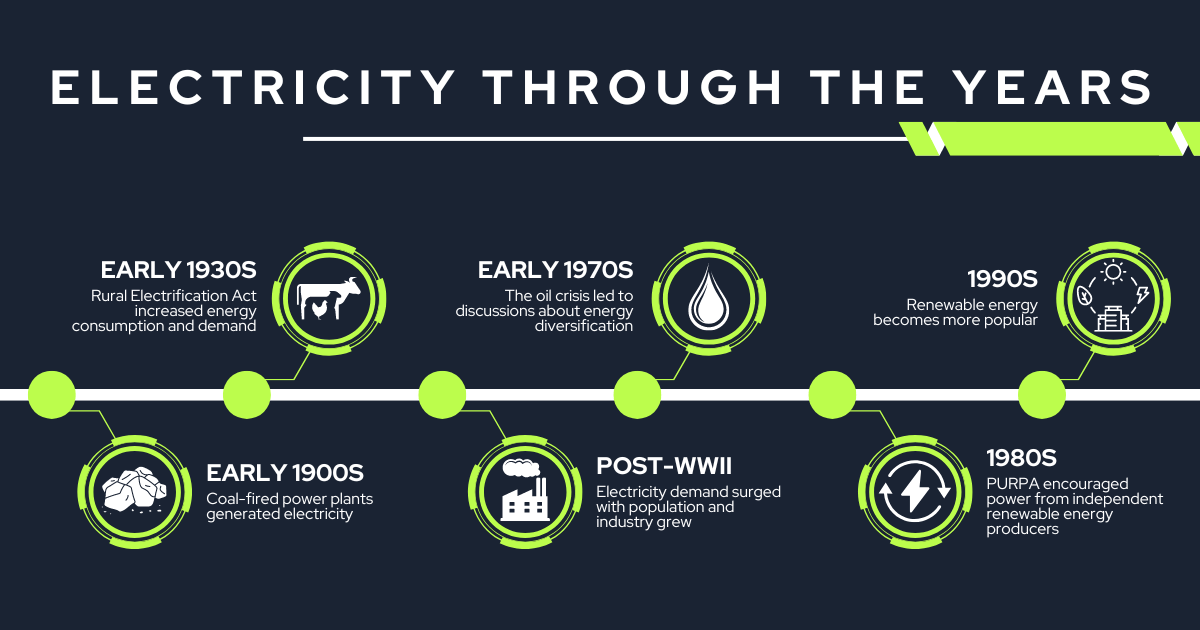
By delving into historical records and imagery, we can visualize the electricity costs in Oklahoma from previous decades. In the early 20th century, energy consumption was primarily driven by the industrial sector and residential demand. Back then, electricity generation relied heavily on coal-fired power plants, which had a significant impact on energy costs and environmental concerns.
The introduction of the Rural Electrification Act in the 1930s played a crucial role in expanding access to electricity across rural areas of Oklahoma. This initiative brought electricity to previously underserved communities, contributing to increased energy consumption and shaping the electricity demand landscape.
In the post-World War II era, electricity demand surged as the state’s population and industries grew. The need for more electricity generation facilities and transmission infrastructure led to changes in pricing structures and the establishment of utilities like Oklahoma Gas & Electric Company (OG&E) as major players in the energy market.
The Impact of Energy Policies on Electricity Costs
Throughout history, energy policies have played a significant role in shaping electricity costs in Oklahoma. In the 1970s, the oil crisis and concerns about energy security led to discussions about diversifying the energy mix. Government policies began promoting energy efficiency and renewable energy sources as a way to reduce dependence on fossil fuels.
The implementation of the Public Utility Regulatory Policies Act (PURPA) in the 1980s encouraged utilities to purchase power from independent renewable energy producers, further paving the way for renewable energy integration in Oklahoma. These policy changes gradually influenced the state’s energy mix and contributed to electricity cost dynamics.
In recent years, Oklahoma has seen further policy developments that impact energy costs. Policies supporting energy efficiency programs and renewable energy tax incentives have incentivized consumers and businesses to adopt greener energy practices, affecting electricity rates positively.
Technological Advancements and Efficiency Improvements
Advancements in technology have revolutionized the energy sector, leading to more efficient energy production, distribution, and consumption. The integration of advanced grid management systems, smart meters, and real-time energy monitoring has enabled better energy demand forecasting and load balancing.
Technological advancements have also enhanced the efficiency of renewable energy sources. Solar panels have become more affordable and efficient, with higher conversion rates of sunlight into electricity. Wind turbines have undergone design improvements, harnessing more energy from the wind. These advancements have contributed to the competitiveness of renewable energy compared to conventional fossil fuel-based generation.
Furthermore, demand-side management technologies and home automation have empowered consumers to take control of their energy usage. Smart home devices, programmable thermostats, and energy-efficient appliances enable homeowners to optimize energy consumption and reduce electricity bills.
The Rise of Renewable Energy and Its Effect on Costs
The growing recognition of environmental concerns and the need to address climate change have driven the rapid adoption of renewable energy sources in Oklahoma. The state’s vast wind resources have positioned it as a leader in wind energy production, with an ever-expanding portfolio of wind farms generating clean electricity.
Additionally, solar energy adoption has accelerated in Oklahoma, driven by falling solar panel costs, net metering policies, and federal tax incentives. Residential, commercial, and utility-scale solar installations have contributed to a diversified energy mix, reducing reliance on traditional fossil fuel-based electricity generation.
The integration of renewable energy sources has impacted electricity costs in multiple ways. First, the declining costs of renewable technologies have helped stabilize electricity rates by providing competitively priced energy. Second, renewable energy production can coincide with periods of high demand, mitigating the need for expensive peaking power plants. Lastly, the environmental benefits of renewables have the potential to reduce external costs associated with pollution and climate change, indirectly affecting electricity rates.
Energy Efficiency Measures: Lowering Electricity Bills
Energy efficiency has become a focal point in reducing energy consumption and lowering electricity bills for consumers and businesses. State and federal energy efficiency programs offer incentives and rebates to encourage energy-conscious practices, ranging from residential retrofits to industrial efficiency upgrades.
Businesses have also embraced energy management strategies to optimize their operations and reduce costs. Energy audits, energy-efficient lighting, and energy management systems are examples of initiatives that can substantially lower electricity expenses for commercial and industrial establishments.
At the residential level, educating consumers about energy-efficient practices and offering incentives for adopting energy-saving technologies can have a significant impact on electricity consumption and expenses. Energy efficiency is an essential component of managing electricity costs sustainably while contributing to the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions.
A Forward Look: Navigating the Future of Energy Expenses
Looking ahead, we envision an energy landscape that continues to evolve in response to technological advancements, policy changes, and shifts in consumer behavior. The ongoing transition to cleaner and more sustainable energy sources will likely influence electricity costs in the future.
As the demand for electricity increases with population growth and economic development, it becomes crucial to adopt innovative solutions to meet this demand efficiently. Investment in energy storage technologies, demand response programs, and grid modernization will play a pivotal role in managing electricity costs while ensuring grid reliability and resilience.
Innovative rate structures and pricing mechanisms, such as real-time pricing and demand-side management programs, could also become more prevalent, allowing consumers to adjust their energy consumption based on electricity prices during different periods of the day or season.